|
|
|
|
|
Contents
1.1 Background
1.2 Project Description
1.3 Scope of the EM&A Report
1.4 Project Organisation
1.5 Summary of Construction Works
1.6 Summary of EM&A Programme Requirements
1.7 Status of Statutory Environmental Compliance with the Environmental Permit
1.8 Status of Other Statutory Environmental Requirements
2.1 Air Quality Monitoring
2.2 Noise Monitoring
2.3 Water Quality Monitoring
2.4 Landfill Gas Monitoring
2.5 Landscape and Visual Monitoring
2.6 EM&A Site Inspection
2.7 Waste Management Status
2.8 Implementation Status of Environmental Mitigation Measures
2.9 Summary of Exceedances of the Environmental Quality Performance Limit
2.10 Summary of Complaints, Notification of Summons and Successful Prosecutions
3.1 Construction Programme for the Coming Month
3.2 Key Issues for the Coming Month
3.3 Monitoring Schedule for the Coming Month
4 Conclusion and Recommendation
Annexes
Annex A Work Programme
Annex B Environmental Mitigation Implementation Schedule
Annex C Monitoring Schedule for This Reporting Period
Annex
D Air Quality
Annex D1 Calibration Certificates for Dust Monitoring
Equipment
Annex D2 24-hour TSP Monitoring Results
Annex D3 Event and Action Plan for Air Quality Monitoring
Annex D4 Meteorological Data
Annex D5 Certificates of the Qualified Odour Panelist
Annex D6 Odour Monitoring Results
Annex D7 Thermal Oxidizer, Landfill Gas Flare and Landfill Gas Generator Stack Emission Monitoring Results
Annex D8 Ambient VOCs, Ammonia and H2S Monitoring Results
Annex
E Noise
Annex E1 Calibration Certificates for Noise Monitoring
Equipment
Annex E2 Noise Monitoring Results
Annex E3 Event and Action Plan for Noise Monitoring
Annex
F Water Quality
Annex F1 Calibration Certificates for Surface Water Quality
Monitoring Equipment
Annex F2 Surface Water Quality Monitoring Results
Annex F3 Event and Action Plan for
Water Quality Monitoring
Annex F4 Calibration Certificates for Effluent Quality Monitoring Equipment
Annex F5 Leachate Levels Monitoring Results
Annex F6 Effluent Quality Monitoring Results
Annex F7 Calibration Certificates for Groundwater Monitoring Equipment
Annex F8 Groundwater Monitoring Results
Annex G
Landfill Gas
Annex G1 Landfill Gas Monitoring Locations for Service Voids,
Utilities and Manholes Along the Site Boundary and Within the SENTX Site
Annex
G2 Calibration Certificates for Landfill Gas Monitoring
Equipment
Annex G3 Landfill Gas Monitoring Results
Annex G4 Event and Action Plan for
Landfill Gas Monitoring
Annex I Monitoring Schedule for the Next Reporting Period
Executive Summary
The SENT Landfill Extension (SENTX) forms an integral part in the Strategic Plan in maintaining the continuity of landfill capacity in the Hong Kong for the cost-effective and environmentally satisfactory disposal of waste. ERM-Hong Kong, Limited (ERM) is commissioned to undertake the role of Environmental Team (ET) for the construction, operation/restoration and aftercare of SENTX Project (“the Project”) in accordance with the requirements specified in the Environmental Permit (EP), updated Environmental Monitoring and Audit (EM&A) Manual, the approved Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report of the Project taking account of the latest design and other relevant statutory requirements. The construction (not including works related to site clearance and preparation) and operation of the Project commenced on 2 January 2019 and 21 November 2021, respectively.
This Monthly EM&A report presents the EM&A works carried out during the period from 1 to 28 February 2022 for the Project in accordance with the updated EM&A Manual.
Exceedance of Action and Limit Levels for Air Quality
No exceedance of Action and Limit Levels for operation/ restoration phase air quality monitoring was recorded in the reporting period.
Exceedance of Action and Limit Levels for Noise
No exceedance of Action and Limit Levels for operation/ restoration phase noise monitoring was recorded in the reporting period.
Exceedance of Action and Limit Levels for Water Quality
Two exceedances of the Limit Level for groundwater (Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)) were recorded for water quality impact monitoring in the reporting period. The groundwater (COD) exceedances at MWX-4 and MWX-6 on 15 February 2022 are under investigation.
Exceedance of Action and Limit Levels for Landfill Gas
No exceedance of Action and Limit Levels for operation/ restoration phase landfill gas monitoring was recorded in the reporting period.
Environmental Complaints, Summons and Prosecutions
There were no complaints, notification of summons or prosecution recorded in the reporting period.
Reporting Change
There was no reporting change in the reporting period.
Future Key Issues
Potential environmental impacts arising from the upcoming construction/ operational activities in the next reporting period of March 2022 are mainly associated with dust emission from the exposed area and loading and unloading operation of dusty materials.
1
Introduction
1.1
Background
The SENT Landfill Extension (SENTX) forms an integral part in the Strategic Plan in maintaining the continuity of landfill capacity in the Hong Kong for the cost-effective and environmentally satisfactory disposal of waste. The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report and the associated Environmental Monitoring and Audit (EM&A) Manual for the construction, operation, restoration and aftercare of the SENTX (hereafter referred to as “the Project”) have been approved under the Environmental Impact Assessment Ordinance (EIAO) in May 2008 (Register No.: AEIAR-117/2008) (hereafter referred to as the approved EIA Report) and an Environmental Permit (EP-308/2008) (EP) was granted by the Director of Environmental Protection (DEP) on 5 August 2008.
Since then, applications for Variation of an Environmental Permit (No. VEP-531/2017) were submitted to EPD and the Variation of Environmental Permits (EP-308/2008/A and EP-308/2008/B) were granted on 6 January 2012 and 20 January 2017, respectively, as the Hong Kong SAR Government has decided to reduce the scale of the design scheme of SENTX assessed in the approved EIA Report and SENTX will only receive construction waste. In May 2018, a Further Environmental Permit (FEP) (FEP-01/308/2008/B) was granted to the SENTX’s contractor, Green Valley Landfill, Limited (GVL).
ERM-Hong Kong, Limited (ERM) and Meinhardt Infrastructure and Environment Limited (Meinhardt) are commissioned to undertake the roles of Environmental Team (ET) and the Independent Environmental Checker (IEC), respectively, to undertake the EM&A activities for the Project in accordance with the requirements specified in the EP, updated EM&A Manual ([1]), approved EIA Report ([2]) taking account of the latest design and other relevant statutory requirements.
1.2
Project Description
The SENTX is a piggyback landfill, occupying the southern part of the existing SENT Landfill (including its infrastructure area) and 13 ha of Tseung Kwan O (TKO) Area 137. A layout plan of the SENTX is shown in Figure 1.1. Under the latest design, the SENTX has a net void capacity of about 6.5 Mm3 and provides an additional lifespan of about 6 years, commencing operation upon exhaustion of the SENT Landfill. The SENTX will receive construction waste only.
The key implementation milestones of the Project are indicatively summarised in Table 1.1. The construction works and operation of the Project commenced on 2 January 2019 and 21 November 2021, respectively.
Table 1.1 Estimated Key Dates of Implementation Programme
|
Key Stage of the Project |
Indicative Date |
|
Start construction |
2 January 2019 |
|
Commissioning of new infrastructure facilities |
2020 |
|
Demolition of existing infrastructure facilities |
2021 |
|
Start waste intake at SENTX |
21 November 2021 |
|
Estimated exhaustion date of SENTX |
2027 |
|
End of aftercare for SENTX |
2057 |
The major construction works of the SENTX includes:
· Site formation at the TKO Area 137 and the existing infrastructure area at SENT Landfill;
· Construction of surface and groundwater drainage systems;
· Construction of the leachate containment and collection systems;
· Construction of new leachate and landfill gas treatment facilities, site offices, maintenance yards at the new infrastructure area;
· Construction of new pipelines to transfer the leachate and landfill gas collected from the existing SENT Landfill to the treatment facilities at the new infrastructure area;
· Construction of the site access and new waste reception facilities; and
· Demolition of the facilities at the existing SENT Landfill infrastructure area.
1.3
Scope of the EM&A Report
This is the Monthly EM&A Report for the Project which summarises the key findings of the EM&A programme during the reporting period from 1 to 28 February 2022 for the construction and operation works.
1.4
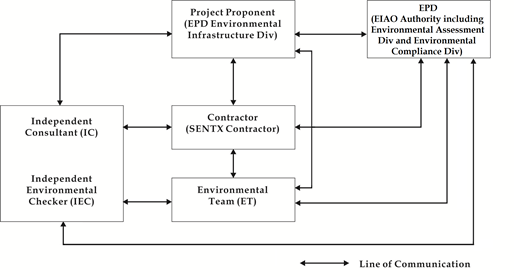
Project Organisation
The organisation structure of the Project is presented in Figure 1.2.
Figure
1.2 Organisation Chart
|
|
Contact details of the key personnel are summarised in Table 1.2 below.
Table 1.2 Contact Information of Key Personnel
|
Party |
Position |
Name |
Telephone |
|
Contractor (Green Valley Landfill Limited) |
Project Manager |
Carl Lai |
2706 8829 |
|
Environmental Team (ET) (ERM-Hong Kong, Limited)
|
ET Leader |
Frank Wan |
2271 3152 |
|
Independent Environmental Checker (IEC) (Meinhardt Infrastructure and Environment Limited)
|
IEC |
W.K. Chiu |
2858 0738 |
1.5
Summary of Construction Works
The programme of the construction is shown in Annex A. As informed by the Contractor, the major works carried out in this reporting period include:
· Rectification of defects at Landfill Gas (LFG) Plant, Leachate Treatment Plant (LTP), infrastructure area and waste reception area;
· Rectification of defects for underground utilities and pipe;
· Construction of MSE wall;
· Site formation for Cell 4X;
· Liner works at Cell 4X;
· Construction of perimeter channel along Western bund of Cell 4X; and
· Maintenance and improvement of temporary surface water drainage.
The implementation schedule of the mitigation measured recommended in the Updated EM&A Manual is presented in Annex B.
1.6
Summary of EM&A Programme Requirements
The status for all environmental aspects are presented in Table 1.3. The EM&A requirements remained unchanged during the reporting period.
Table 1.3 Summary of Status for the Environmental Aspects under the Updated EM&A Manual
|
Parameters |
Status |
|
Air Quality |
|
|
Baseline Monitoring |
The results of baseline air quality monitoring were reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and Pre-operation Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.3 |
|
Impact Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Noise |
|
|
Baseline Monitoring |
The results of baseline noise monitoring were reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.3 |
|
Impact Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Water Quality |
|
|
Baseline Monitoring |
The results of baseline surface water quality monitoring were reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and Pre-operation Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.3 |
|
Impact Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Landfill Gas |
|
|
Impact Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Waste Management |
|
|
Waste Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Landscape and Visual |
|
|
Baseline Monitoring |
The results of baseline landscape and visual monitoring were reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.3 |
|
Operation Phase Audit |
On-going |
|
Site Environmental Audit |
|
|
Regular Site Inspection |
On-going |
|
Complaint Hotline and Email Channel |
On-going |
|
Environmental Log Book |
On-going |
Taking into account the operation works, impact monitoring of air quality, noise, water quality, landfill gas and waste management were carried out in the reporting period. The impact monitoring schedule of air quality, noise, water quality and landfill gas monitoring are provided in Annex C.
The EM&A programme also involved environmental site inspections and related auditing conducted by the ET for checking the implementation of the required environmental mitigation measures recommended in the approved EIA Report and relevant EP submissions. To promote the environmental awareness and enhance the environmental performance of the contractors, environmental trainings and regular environmental management meetings were conducted during the reporting period, which are summarised as below:
Ÿ One environmental management meeting was held with the Contractor, ER, ET, IEC and EPD on 24 February 2022; and
Ÿ Environmental toolbox trainings on Quality Powered Mechanical Equipment (QPME) and Good Vehicle Maintenance Practices were provided on 9 February and 23 February 2022 respectively by the Contractor to the workers.
1.7
Status of Statutory Environmental Compliance with the
Environmental Permit
The status of statutory environmental compliance with the EP conditions under the EIAO, submission status under the EP and implementation status of mitigation measures are presented in Table 1.4.
Table 1.4 Status of Submissions required under the EP and Implementation Status of Mitigation Measures
|
EP Condition |
Submission / Implementation Status |
Status |
|
2.3 |
Management Organisation of Main Construction Companies |
Submitted and accepted by EPD. |
|
2.4 |
Setting up of Community Liaison Group |
Community Liaison Group was set up. |
|
2.5 |
Submission of Detailed Landfill Gas Hazard Assessment Report |
Submitted and accepted by EPD on 10 January 2019. |
|
2.6 |
Submission of Restoration and Ecological Enhancement Plan |
Submitted to EPD on 28 June 2019. |
|
2.7 |
Setting up of Trial Nursery |
Trial Nursery works was commenced on 28 August 2019. |
|
2.8 |
Advance Screen Planting |
Advance Screen Planting works were completed on 28 June 2019. |
|
2.9 |
Provision of Multi-layer Composite Liner System |
Under implementation. |
1.8
Status of Other Statutory Environmental Requirements
The environmental licenses and permits (including EP, Water Pollution Control Ordinance (WPCO) discharge license, registration as a chemical waste producer, and construction noise permit) that are valid in the reporting period are presented in Table 1.5. No non-compliance with environmental statutory requirements was identified.
Table 1.5 Status of Statutory Environmental Requirements
|
Description |
Ref No. |
Status |
|
Environmental Permit |
EP-308/2008 |
Granted on 5 August 2008 |
|
Variation of Environmental Permit |
EP-308/2008/A |
Granted on 6 January 2012 |
|
EP-308/2008/B |
Granted on 20 January 2017 |
|
|
Further Environmental Permit |
FEP-01/308/2008/B |
Granted on 16 May 2018 |
|
Water Discharge License under WPCO (Permit Holder: GVL) |
Licence No.: WT00036269-2020 |
Validity from 21 June 2020 to 30 June 2022 |
|
Billing Account for Disposal of Construction Waste |
Chit Account Number: 5001692 |
Approved on 28 December 2005 |
|
Registration as a Chemical Waste Producer (Permit Holder: Chun Wo) |
5213-839-C3507-10 |
Issued on 23 August 2018 |
|
Registration as a Chemical Waste Producer (Permit Holder: REC) |
5518-839-R2289-06 |
Issued on 24 October 2019 |
|
Construction Noise Permit (Permit Holder: GVL) |
GW-RE1316-21 |
Validity from 5 January 2022 to 14 June 2022 |
|
Construction Noise Permit (Permit Holder: Paul Y.) |
GW-RE1138-21 |
Validity from 16 November 2021 to 15 February 2022 |
2
EM&A Results
The EM&A programme for the Project required environmental monitoring for air quality, noise, water quality and landfill gas as well as environmental site inspections for air quality, noise, water quality, landfill gas, waste management, and landscape and visual impacts. The EM&A requirements and related findings for each component are summarised in the following sections.
2.1
Air Quality Monitoring
2.1.1
Dust Monitoring
Monitoring Requirements and
Equipment
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project, impact dust monitoring (in term of Total Suspended Particulates (TSP)) was carried out at the four designated locations along the site boundary (i.e. AM1, AM2, AM3 and AM4) during the operation/restoration phase, at a 6-day interval.
The Action and Limit Levels of the dust monitoring is provided in Table 2.1 below.
Table 2.1 Action and Limit Levels for 24-hour TSP
|
Monitoring Station |
Action Level |
Limit Level |
|
AM1 - SENTX Site Boundary (North) |
260 µg m-³ |
260 µg m-³ |
|
AM2 - SENTX Site Boundary (West, near DP3) |
||
|
AM3 - SENTX Site Boundary (West, near RC15) |
||
|
AM4 - SENTX Site Boundary (West, near EPD building) |
High volume air samplers (HVSs) in compliance with the specifications listed under Section 3.2.2 of the updated EM&A Manual were used to measure 24-hour TSP levels at the dust monitoring stations. The HVSs were calibrated upon installation and thereafter at bi-monthly intervals to check the validity and accuracy of the results.
The equipment used in the impact dust monitoring programme and monitoring locations are summarised in Table 2.2 and illustrated in Figure 2.1, respectively. Copies of the calibration certificates for the equipment are presented in Annex D1.
Table 2.2 Dust Monitoring Details
|
Monitoring Station |
Location |
Parameter |
Frequency and Duration |
Monitoring Dates |
Equipment |
|
AM1 |
SENTX Site Boundary (North) |
24-hour TSP |
Once every 6 days |
5, 11, 17, 23 Feb 2022 |
Tisch TE-5170 (S/N: 1190) |
|
AM2 |
SENTX Site Boundary (West, near DP3) |
Tisch TE-5170 (S/N: 1047) |
|||
|
AM3 |
SENTX Site Boundary (West, near RC15) |
Tisch TE-5170 (S/N: 1258) |
|||
|
AM4 |
SENTX Site Boundary (West, near EPD building) |
Tisch TE-5170 (S/N: 1101) |
Monitoring Schedule for the
Reporting Month
The schedule for dust monitoring during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
Results and Observations
The monitoring results for 24-hour TSP are summarised in Table 2.3. The detailed monitoring results and the graphical presentation of the 24-hour TSP results at each monitoring location are provided in Annex D2.
Table 2.3 Summary of 24-hour TSP Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
Monitoring Station |
Average 24-hr TSP Concentration (µg m-3) (Range in bracket) |
Action Level (µg/m3) |
Limit Level (µg/m3) |
|
AM1 - SENTX Site Boundary (North) |
73 (42 – 132) |
260 |
260 |
|
AM2 - SENTX Site Boundary (West, near DP3) |
56 (32 – 85) |
260 |
260 |
|
AM3 - SENTX Site Boundary (West, near RC15) |
100 (57 – 140) |
260 |
260 |
|
AM4 - SENTX Site Boundary (West, near EPD building) |
75 (47 – 107) |
260 |
260 |
The major dust sources in the reporting period included fugitive dust emission from exposed area in SENTX, as well as nearby operations of the SENTX and the TKO Area 137 Fill Bank.
All the 24-hour TSP results were below the Action and Limit Levels at the monitoring locations in the reporting period. No action is thus required to be undertaken in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex D3.
Meteorological Data
Meteorological data obtained from the SENTX on-site meteorological monitoring station was used for the dust monitoring and is shown in Annex D4. It is considered that meteorological data obtained at the on-site meteorological monitoring station is representative of the Project area and could be used for the operation/restoration phase dust monitoring programme for the Project.
2.1.2
Odour
Monitoring
Monitoring Requirements
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project, odour patrol was carried out along the site boundary during the operation/ restoration phase. During the first month of operation, daily odour patrol (3 times per day) was conducted jointly by the ET and the IEC. The odour intensity detected was based on that determined by the IEC. In addition, an independent party (ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd.) was appointed to undertake odour patrol together with the ET and IEC three times per week. During these patrols, the odour intensity detected was based on that determined by the independent third party.
Reduction of odour monitoring frequency from Period 1 (daily, three times per day) to Period 2 (weekly)) was approved by EPD on 4 February 2022. Weekly odour patrol was conducted jointly by the ET and the IEC from 4 February 2022. In addition, an independent party (ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd.) was appointed to undertake odour patrol together with the ET and IEC once every two weeks.
The Action and Limit Levels for odour patrol is provided in Table 2.4 below.
Table 2.4 Action and Limit Levels for Odour Patrol
|
Parameter |
Action Level |
Limit Level |
|
Perceived odour intensity and odour complaints |
· Odour intensity ≥ Class 2 recorded; or · One documented complaint received |
· Odour intensity ≥ Class 3 recorded on 2 consecutive patrol (a) (b)
|
|
Notes: (a) i.e. either Class 3-strong or Class 4-extreme odour intensity. (b) The exceedances of the odour intensity do not need to be recorded at the same location. |
||
Odour patrol was conducted by trained personnel / competent persons with a specific sensitivity to a reference odour (i.e. on reference materials n-butanol with the concentration of 50ppm in nitrogen (v/v)) in compliance with Section 3.7.2 of the updated EM&A Manual patrolling and sniffing along the SENTX Site boundary to detect any odour.
The odour monitoring programme and patrol route are summarised in Table 2.5 and illustrated in Figure 2.2 respectively. Copies of the certificates of the qualified odour panelist are presented in Annex D5.
Table 2.5 Odour Monitoring Details
|
Patrol Locations |
Parameters |
Patrol Frequency (a) |
Monitoring Dates and Time |
|
Patrol along the SENTX Site Boundary (Checkpoints OP1 – OP11) |
Odour Intensity (see Table 2.6) |
Period 1 - First month of operation Daily, three times a day in the morning, afternoon and evening/night (between 18:00 and 22:00 hrs) conducted by the ET and the IEC
Three times per week on different days conducted by an independent third party together with the ET and IEC (b)
Period 2 - Three months following period 1 (c)
Weekly conducted by the ET and the IEC
Once every two weeks conducted by an independent third party together with the ET and IEC (b)
Period 3 - Throughout operation following period 2 (c) Monthly conducted by the ET and the IEC
Quarterly conducted by an independent third party together with the ET and IEC (b) |
Conducted by ET & IEC: 1 – 4 Feb 2022 (10:30 – 12:00, 14:30 – 16:00, 18:00 – 19:30), 18, 28 Feb 2022
Conducted by an independent third party, ET & IEC: 4 Feb 2022 (10:00 – 12:00), 11, 21 Feb 2022 |
|
Notes: (a) Reduction of monitoring frequency will be subject to the monitoring results to demonstrate environmentally acceptable performance. (b) Patrol shall be scheduled so that they are carried out together with the patrols to be carried out jointly by the ET and the IEC. (c) Commencement of each period will be justified by the ET Leader and verified by the IEC and will be subject to agreement with the EPD (EIAO Authority) and Project Proponent. |
|||
Table 2.6 Odour Intensity Level
|
Class |
Odour Intensity |
Description |
|
0 |
Not Detected |
No odour perceived or an odour so weak that it cannot be easily characterised or described. |
|
1 |
Slight |
Identified odour, slight |
|
2 |
Moderate |
Identified odour, moderate |
|
3 |
Strong |
Identified odour, strong |
|
4 |
Extreme |
Severe odour |
Monitoring Schedule for the
Reporting Month
The schedule for odour patrol during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
Results and Observations
The odour monitoring results are summarised and provided in Table 2.7 and Annex D6, respectively.
Table 2.7 Summary of Odour Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
Odour Checkpoints |
Odour Intensity Class (Range) |
Action Level |
Limit Level |
|
OP1 |
0 |
Odour intensity ≥ Class 2 recorded |
Odour intensity ≥ Class 3 recorded on 2 consecutive patrol |
|
OP2 |
0 |
||
|
OP3 |
0 |
||
|
OP4 |
0 |
||
|
OP5 |
0 |
||
|
OP6 |
0 |
||
|
OP7 |
0 |
||
|
OP8 |
0 |
||
|
OP9 |
0 – 1 |
||
|
OP10 |
0 |
||
|
OP11 |
0 – 1 |
|
|
The potential odour sources in the reporting period included the operation of generator at SENTX, as well as nearby operations of the Town Gas Plant.
All the odour monitoring results were below the Action and Limit Levels in the reporting period. No action is thus required to be undertaken in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex D3.
2.1.3
Thermal Oxidiser, Landfill Gas
Flare and Landfill Gas Generator Stack Emission Monitoring
Monitoring Requirements and
Equipment
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project, the performance of the thermal oxidiser, landfill gas flare and landfill gas generator was monitored when they are in operation. Gas samples were collected from the stack of the thermal oxidizer, landfill gas flare and landfill gas generator for laboratory analysis for NO2, CO, SO2, Benzene and Vinyl chloride and in-situ analysis for exhaust gas velocity at monthly interval and for laboratory analysis for non-methane organic compounds and ammonia (for thermal oxidizer only) at quarterly interval. The operating conditions of the thermal oxidiser, landfill gas flare and landfill gas generator were also monitored continuously.
The Limit Levels for stack emission of the thermal oxidiser, landfill gas flare and landfill gas generator are provided in Tables 2.8 – 2.10 below.
Table 2.8 Limit Levels for Stack Emission of the Thermal Oxidiser
|
Parameters |
Limit Level |
|
NO2 |
1.58 gs-1 |
|
CO |
0.53 gs-1 |
|
SO2 |
0.07 gs-1 |
|
Benzene |
3.01 x 10-2 gs-1 |
|
Vinyl chloride |
2.23 x 10-3 gs-1 |
|
Gas combustion temperature |
850oC (minimum) |
|
Exhaust gas exit temperature |
443K (minimum) (a) |
|
Exhaust gas velocity |
7.5 ms-1 (minimum) (a) |
|
Note: (a) Level under full load condition. |
|
Table 2.9 Limit Levels for Stack Emission of the Landfill Gas Flare
|
Parameters |
Limit Level |
|
NO2 |
0.97 gs-1 |
|
CO |
2.43 gs-1 |
|
SO2 |
0.22 gs-1 |
|
Benzene |
4.14 x 10-4 gs-1 |
|
Vinyl Chloride |
2.60 x 10-4 gs-1 |
|
Gas combustion temperature |
815oC (minimum) |
|
Exhaust gas exit temperature |
923 K (minimum) (a) |
|
Exhaust gas velocity |
9.0 m s-1 (minimum) (a) |
|
Note: (a) Level under full load condition. |
|
Table 2.10 Limit Levels for Stack Emission of the Landfill Gas Generator
|
Parameters |
Limit Level |
|
NO2 |
1.91 gs-1 |
|
CO |
2.48 gs-1 |
|
SO2 |
0.528 gs-1 |
|
Benzene |
2.47 x 10-4 gs-1 |
|
Vinyl chloride |
1.88 x 10-5 gs-1 |
|
Gas combustion temperature |
450oC (minimum) |
|
Exhaust gas exit temperature |
723K (minimum) (a) |
|
Exhaust gas velocity |
30.0 ms-1 (minimum) (a) |
|
Note: (a) Level under full load condition. |
|
Gas samples were collected from the centroid of the stack with stainless steel sampling probe, into inert sample containers (i.e. Canister and Tedlar Bag) and transferred to ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. (HOKLAS Registration No. 066) laboratory within 24 hours of collection for direct analysis on a gas chromatography within 48 hours after collection. The flue gas velocity of the gas stream at the exhaust of thermal oxidize was determined by S-Pitot tube during the emission sampling.
The stack emission monitoring programme and monitoring locations are summarised in Table 2.11 and illustrated in Figure 2.1, respectively.
Table 2.11 Thermal Oxidiser, Landfill Gas Flare and Landfill Gas Generator Stack Emission Monitoring Details
|
Monitoring Location |
Parameter |
Frequency |
Monitoring Date |
|
Stack of Thermal Oxidiser |
Laboratory analysis for · NO2 · CO · SO2 · Benzene · Vinyl chloride In-situ analysis for · Exhaust gas velocity |
Monthly for the first 12 months of operation and thereafter at quarterly intervals |
11 Feb 2022 |
|
Laboratory analysis for · Non-methane organic compounds |
Quarterly for the 1st year of operation (b) |
11 Feb 2022 |
|
|
Laboratory analysis for · Ammonia |
Quarterly |
11 Feb 2022 |
|
|
· Gas combustion temperature · Exhaust temperature · Exhaust gas velocity (a) |
Continuously |
1 – 28 Feb 2022 |
|
|
Stack of Landfill Gas Flare |
Laboratory analysis for · NO2 · CO · SO2 · Benzene · Vinyl chloride In-situ analysis for · Exhaust gas velocity |
Monthly for the first 12 months of operation and thereafter at quarterly intervals |
11 Feb 2022 |
|
Laboratory analysis for · Non-methane organic compounds |
Quarterly for the 1st year of operation (b) |
11 Feb 2022 |
|
|
· Gas combustion temperature · Exhaust temperature · Exhaust gas velocity (a) |
Continuously |
1 – 28 Feb 2022 |
|
|
Stack of Landfill Gas Generator |
Laboratory analysis for · NO2 · CO · SO2 · Benzene · Vinyl chloride In-situ analysis for · Exhaust gas velocity |
Monthly for the first 12 months of operation and thereafter at quarterly intervals |
11 Feb 2022 |
|
Laboratory analysis for · Non-methane organic compounds |
Quarterly for the 1st year of operation (b) |
11 Feb 2022 |
|
|
· Exhaust temperature · Exhaust gas velocity (a) |
Continuously |
1 – 28 Feb 2022 |
|
|
Notes: (a) The exhaust gas velocity is calculated based on the cross-section area of the stack and continuous monitored gas flow and combustion temperature data. (b) The monitoring results will be reviewed towards the end of the first year of operation to determine if monitoring of this parameter can be terminated upon agreement by the EIAO Authority, IEC and Project Proponent. |
|||
Monitoring Schedule for the
Reporting Month
The schedule for thermal oxidizer, landfill gas flare and landfill gas generator stack emission monitoring during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
Results and Observations
The thermal oxidizer, landfill gas flare and landfill gas generator stack emission monitoring results and detailed continuous monitoring results are summarised in Tables 2.12 - 2.14 and provided in Annex D7, respectively.
Table 2.12 Summary of Thermal Oxidiser Stack Emission Monitoring in the Reporting Period
|
Parameters |
Monitoring Results (Range in Bracket) |
Limit Level |
|
NO2 |
1.17 gs-1 |
1.58 gs-1 |
|
CO |
0.06 gs-1 |
0.53 gs-1 |
|
SO2 |
0.02 gs-1 |
0.07 gs-1 |
|
Benzene |
<3 x 10-5 gs-1 |
3.01 x 10-2 gs-1 |
|
Vinyl chloride |
<3 x 10-5 gs-1 |
2.23 x 10-3 gs-1 |
|
Non-methane Organic Carbons |
3.6 x 10-3 gs-1 |
- |
|
Ammonia |
6.52 x 10-2 gs-1 |
- (c) |
|
Gas combustion temperature |
973oC (958oC – 1,013oC) |
850oC (minimum) |
|
Exhaust gas exit temperature |
1,230K (1,219K – 1,241K) |
443K (minimum) (a) |
|
Exhaust gas velocity |
9.9 ms-1 (b) |
7.5 ms-1 (minimum) (a) |
|
Notes: (a) Level under full load condition. (b) The exhaust gas velocity was calculated based on the cross-section area of the stack and the gas flow and combustion temperature data measured during the stack emission monitoring. The limit level was not applicable as the stack was not operated under full load condition. (c) The emission limit for ammonia is under review and will be supplemented in subsequent revision. |
||
Table 2.13 Summary of Landfill Gas Flare Stack Emission Monitoring in the Reporting Period
|
Parameters |
Monitoring Results (Range in Bracket) |
Limit Level |
|
NO2 |
<0.01 gs-1 |
0.97 gs-1 |
|
CO |
0.027 gs-1 |
2.43 gs-1 |
|
SO2 |
0.110 gs-1 |
0.22 gs-1 |
|
Benzene |
5.1 x 10-5 gs-1 |
4.14 x 10-4 gs-1 |
|
Vinyl chloride |
<1.1 x 10-5 gs-1 |
2.60 x 10-4 gs-1 |
|
Non-methane Organic Carbons |
4.1 x 10-3 gs-1 |
- |
|
Gas combustion temperature |
Flare 1: 893oC (816oC – 995oC) Flare 2: 857oC (830oC – 924oC) |
815oC (minimum) |
|
Exhaust gas exit temperature |
Flare 1: 1,143K (1,083K – 1,213K) Flare 2: 1,072K (1,015K – 1,123K) |
923 K (minimum) (a) |
|
Exhaust gas velocity |
4.4 ms-1 (b) |
9.0 m s-1 (minimum) (a) |
|
Note: (a) Level under full load condition. (b) The exhaust gas velocity was calculated based on the cross-section area of the stack and the gas flow and combustion temperature data measured during the stack emission monitoring. The limit level was not applicable as the stack was not operated under full load condition. |
||
Table 2.14 Summary of Landfill Gas Generator Stack Emission Monitoring in the Reporting Period
|
Parameters |
Monitoring Results (Range in Bracket) |
Limit Level |
|
NO2 |
0.016 gs-1 |
1.91 gs-1 |
|
CO |
0.056 gs-1 |
2.48 gs-1 |
|
SO2 |
0.002 gs-1 |
0.528 gs-1 |
|
Benzene |
<3 x 10-6 gs-1 |
2.47 x 10-4 gs-1 |
|
Vinyl chloride |
<2 x 10-6 gs-1 |
1.88 x 10-5 gs-1 |
|
Non-methane Organic Carbons |
2 x 10-4 gs-1 |
- |
|
Exhaust gas exit temperature |
843K (836K – 847K) |
723K (minimum) (a) |
|
Exhaust gas velocity |
11.9 ms-1 (b) |
30.0 ms-1 (minimum) (a) |
|
Note: (a) Level under full load condition. (b) The exhaust gas velocity was calculated based on the cross-section area of the stack and the gas flow and combustion temperature data measured during the stack emission monitoring. The limit level was not applicable as the stack was not operated under full load condition. |
||
All thermal oxidizer, landfill gas flare and landfill gas generator stack emission monitoring results were below the Limit Levels in the reporting period. No action is thus required to be undertaken in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex D3.
2.1.4
Ambient
VOCs, Ammonia and H2S Monitoring
Monitoring Requirements and
Equipment
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project, ambient VOCs, ammonia and H2S monitoring was carried out at the four designated locations along the site boundary (i.e. AM1, AM2, AM3 and AM4) during the operation/restoration phase, at quarterly interval.
The Limit Levels for ambient VOCs, ammonia and H2S monitoring is provided in Table 2.15 below.
Table 2.15 Provisional Limit Levels for Ambient VOCs, Ammonia and H2S Monitoring
|
Parameters |
Limit Level (µg m-³) (a) |
|
Methane |
NA (b) |
|
Ammonia |
180 |
|
H2S |
42 |
|
Dichlorodifluoro-methane |
NA (b) |
|
Vinyl Chloride |
26 |
|
Methanol |
2,660 |
|
Ethanol |
19,200 |
|
Dimethylsulphide |
NA (b) |
|
Carbon Disulphide |
150 |
|
Methylene Chloride |
3,530 |
|
Chloroform |
99 |
|
Methyl propionate |
NA (b) |
|
Butan-2-ol |
3,080 |
|
1.1.1-Trichloroethane |
5,550 |
|
1.2-Dichloroethane |
210 |
|
Benzene |
33 |
|
Carbon Tetrachloride |
64 |
|
Dipropyl ether |
NA (b) |
|
Heptane |
20,850 |
|
Trichloroethylene |
5,500 |
|
Ethyl propionate |
NA (b) |
|
Methyl butanoate |
NA (b) |
|
Methanethiol |
10 |
|
Toluene |
1,910 |
|
Ethyl butanoate |
NA (b) |
|
Propyl benzene |
NA (b) |
|
Octane |
NA (b) |
|
Propyl propionate |
NA (b) |
|
1.2-Dibromoethane (EDB) |
39 |
|
Butyl acetate |
7,240 |
|
Tetrachloroethylene |
1,380 |
|
Ethyl benzene |
4,410 |
|
Nonane |
NA (b) |
|
Ethanethiol |
13 |
|
Decanes |
NA (b) |
|
Limonene |
NA (b) |
|
Butyl benzene |
NA (b) |
|
Undecane |
NA (b) |
|
Butanethiol |
NA (b) |
|
Terpenes |
NA (b) |
|
Xylenes |
2,200 |
|
Dichlorobenzene |
120 |
|
Notes: (a) Provisional Limit Levels established in the Pre-operation Baseline Monitoring Report. (b) No relevant WHO/USEPA/CARB’s ambient criteria and WEL available. |
|
VOCs
Ambient air samples were drawn into the pre-cleaned and vacuum canister directly when the valve of the flow controller (with preset flow rate) was opened. After sampling, the valve will be closed manually and the canister with VOCs gas samples were transported for laboratory analysis.
Methane
Pre-cleaned Tedlar bag was placed in the vacuum chamber. Ambient air was collected in the Tedlar bag under the vacuum condition when the pump is switched on. The Tedlar bag was filled up to 90% of total capacity to avoid leakage and bag deformation. After sampling, pump is switched off and the valve of Tedlar bag was closed manually. The air samples were transported back to laboratory for analysis.
Ammonia
Calibrated personal air pump was used to pump the air through a sulfuric acid-treated silica gel sorbent tube. Gaseous ammonia in air was then trapped in the sorbent tube. The tube was transported back to laboratory for analysis.
H2S
H2S in air is collected in mid-get impingers by aspirating a measured volume of air through an alkaline suspension of cadmium hydroxide (as the absorbing solution). The sulphide is precipitated as cadmium sulphide to prevent air oxidation of the sulphide. Arabinogalactan is added to the cadmium hydroxide slurry prior to sampling to minimize photo-decomposition of the precipitated cadmium sulphide. The solution is transported back to laboratory for analysis.
All air samples collected for laboratory analysis were transported to ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. (HOKLAS Registration No. 066) laboratory within 24 hours and analysed within 48 hours.
The ambient VOCs, ammonia and H2S monitoring programme and monitoring locations are summarised in Table 2.16 and illustrated in Figure 2.1, respectively.
Table 2.16 Ambient VOCs, Ammonia and H2S Monitoring Details
|
Monitoring Station |
Location |
Parameter |
Frequency |
Monitoring Date |
|
||
|
AM1 |
SENTX Site Boundary (North) |
· Methane · Ammonia · A suite of VOCs (a) · H2S |
Quarterly |
15 Feb 2022 |
|
||
|
AM2 |
SENTX Site Boundary (West, near DP3) |
|
|||||
|
AM3 |
SENTX Site Boundary (West, near RC15) |
|
|||||
|
AM4 |
SENTX Site Boundary (West, near EPD building) |
|
|||||
|
Notes: (a) A suite of VOCs includes: |
|
||||||
|
· Trichloroethylene · Vinyl chloride · Methylene chloride · Chloroform · 1,2-dichloroethane · 1,1,1-trichloroethane · Carbon tetrachloride · Tetrachloroethylene · 1,2-dibromoethane · Benzene · Toluene · Carbon disulphide · Propyl benzene · Ethyl benzene |
· Butyl benzene · Xylenes · Decanes · Undecane · Limonene · Terpenes · Ethanol · Butan-2-ol · Dimethylsulphide · Methyl propionate · Ethyl propionate · Propyl propionate · Butyl acetate · Ethyl butanoate |
· Dichlorobenzene · Methyl butanoate · Dipropyl ether · Methanethiol · Ethanethiol · Butanethiol · Methanol · Heptanes · Octanes · Nonanes · Dichlorodifluoro-methane · Methane |
|||||
Monitoring Schedule for the
Reporting Month
The schedule for ambient VOCs, ammonia and H2S monitoring during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
Results and Observations
The ambient VOCs, ammonia and H2S monitoring results are summarised in Tables 2.17 and provided in Annex D8.
Table 2.17 Summary of Ambient VOCs, Ammonia and H2S Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
Parameters |
Limit Level (µg m-³) (a) |
Monitoring Results (µg m-³) |
||||
|
AM1 |
AM2 |
AM3 |
AM4 |
|||
|
Methane |
NA (b) |
0.00068% (v/v) |
0.00031% (v/v) |
0.00020% (v/v) |
0.00020% (v/v) |
|
|
Ammonia |
180 |
<10 |
<10 |
<10 |
<10 |
|
|
H2S |
42 |
<14 |
<14 |
<14 |
<14 |
|
|
1.1.1-Trichloroethane |
5,550 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
|
|
1.2-Dibromoethane (EDB) |
39 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
|
1.2-Dichloroethane |
210 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
|
|
Benzene |
33 |
2.0 |
1.5 |
1.2 |
1.5 |
|
|
Butan-2-ol |
3,080 |
<0.6 |
<0.6 |
<0.6 |
<0.6 |
|
|
Butanethiol |
NA (b) |
<1.2 |
<1.2 |
<1.2 |
<1.2 |
|
|
Carbon Disulphide |
150 |
1.8 |
1.2 |
0.8 |
1.2 |
|
|
Carbon Tetrachloride |
64 |
0.7 |
0.8 |
0.7 |
0.8 |
|
|
Chloroform |
99 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
|
|
Decanes |
NA (b) |
0.7 |
<0.7 |
1.8 |
<0.7 |
|
|
Dichlorobenzene |
120 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Dichlorodifluoro-methane |
NA (b) |
1.3 |
1.8 |
1.3 |
1.9 |
|
|
Dimethylsulphide |
NA (b) |
<0.2 |
<0.2 |
<0.2 |
<0.2 |
|
|
Dipropyl ether |
NA (b) |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
|
|
d-Limonene |
NA (b) |
0.8 |
<0.4 |
0.9 |
<0.4 |
|
|
Ethanethiol |
13 |
<0.6 |
<0.6 |
<0.6 |
<0.6 |
|
|
Ethanol |
19,200 |
8.2 |
<3.8 |
<3.8 |
<3.8 |
|
|
Ethyl butanoate |
NA (b) |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Ethyl propionate |
NA (b) |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
|
|
Ethylbenzene |
4,410 |
0.9 |
0.6 |
1.5 |
0.6 |
|
|
Heptane |
20,850 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
|
|
Methanethiol |
10 |
<0.4 |
<0.4 |
<0.4 |
<0.4 |
|
|
Methanol |
2,660 |
13.3 |
29.9 |
37.2 |
22.0 |
|
|
Methyl butanoate |
NA (b) |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
|
|
Methyl propionate |
NA (b) |
<0.7 |
<0.7 |
<0.7 |
<0.7 |
|
|
Methylene Chloride |
3,530 |
2.4 |
3.0 |
2.9 |
3.2 |
|
|
n-Butyl acetate |
7,240 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
|
n-Butyl benzene |
NA (b) |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Nonane |
NA (b) |
<0.9 |
<0.9 |
<0.9 |
<0.9 |
|
|
n-Propyl benzene |
NA (b) |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
<0.8 |
|
|
Octane |
NA (b) |
<0.9 |
<0.9 |
<0.9 |
<0.9 |
|
|
Propyl propionate |
NA (b) |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Terpenes |
NA (b) |
2.3 |
0.9 |
0.9 |
<0.8 |
|
|
Tetrachloroethylene |
1,380 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
<0.7 |
|
|
Toluene |
1,910 |
1.7 |
1.5 |
2.8 |
1.9 |
|
|
Trichloroethylene |
5,500 |
<1.1 |
<1.1 |
<1.1 |
<1.1 |
|
|
Undecane |
NA (b) |
<1.2 |
<1.2 |
<1.2 |
<1.2 |
|
|
Vinyl Chloride |
26 |
<0.3 |
<0.3 |
<0.3 |
<0.3 |
|
|
Xylenes |
2,200 |
2.3 |
1.6 |
3.5 |
1.0 |
|
|
Notes: (a) Provisional Limit Levels established in the Pre-operation Baseline Monitoring Report. (b) No relevant WHO/USEPA/CARB’s ambient criteria and WEL available. |
||||||
All ambient VOCs, ammonia and H2S monitoring results were below the Limit Levels in the reporting period. No action is thus required to be undertaken in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex D3.
2.2
Noise Monitoring
2.2.1
Monitoring Requirements and Equipment
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project, impact noise monitoring was conducted weekly at the monitoring location (i.e. NM1) to obtain one set of 30 minutes measurement between 07:00 and 19:00 hours on normal weekdays.
The Action and Limit Levels for operational noise of the Project are provided in Table 2.18 below.
Table 2.18 Action and Limit Levels for Operational Noise
|
Time Period |
Action Level (a) |
Limit Level (b) |
|
07:00 – 19:00 hrs on all days
|
When one documented complaint is received from any one of the noise sensitive receivers (NSRs) or 75 dB(A) recorded at the monitoring station |
65 dB(A) at NSRs (c) |
|
19:00 – 23:00 hrs on all days
|
65 dB(A) at NSRs (c) |
|
|
23:00 – 07:00 hrs on all days |
55 dB(A) at NSRs (c) |
|
|
Notes: (a) 75dB(A) along and at about 100m from the SENTX site boundary was set as the Action Level. (b) Limits specified in the GW-TM and IND-TM for construction and operational noise, respectively. (c) Limit Level only apply to operational noise without road traffic and construction activities noise. |
||
Noise monitoring was performed by ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. (HOKLAS Registration No. 066) using sound level meter at the designated monitoring station NM1 (see Figure 2.1) in accordance with the requirements stipulated in the updated EM&A Manual. Acoustic calibrator was deployed to check the sound level meter at a known sound pressure level. Details of the deployed equipment are provided in Table 2.19. Copies of the calibration certificates for the equipment are presented in Annex E1.
Table 2.19 Noise Monitoring Details
|
Monitoring Station (1) |
Location |
Parameter |
Frequency and Duration |
Monitoring Dates |
Equipment |
|
NM1 |
SENTX Site Boundary (North) |
Leq (30 min) measurement between 07:00 and 19:00 hours on normal weekdays (Monday to Saturday) |
Once per week for 30 mins during operation of the Project |
7, 14, 24 Feb 2022 |
Sound Level Meter: Rion NL-52 (S/N: 00921191)
Acoustic Calibrator: Rion NC-74 (S/N: 34246492)
|
2.2.2
Monitoring Schedule for the Reporting Month
The schedule for noise monitoring during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
2.2.3
Results and Observations
A total of 3 impact noise monitoring events were scheduled during the reporting period. However, noise monitoring on 7 February 2022 was cancelled due to adverse weather condition. Results for noise monitoring are summarised in Table 2.20. The monitoring results and the graphical presentation of the data are provided in Annex E2.
Table 2.20 Summary of Operation Noise Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
Monitoring Station |
Measured Noise Level Leq (30 min), dB(A) |
||
|
Average |
Range |
Action and Limit Level |
|
|
NM1 |
48.6 |
48.1 – 29.0 |
75 |
Major noise sources identified during the noise monitoring included noise from operations of the SENTX and the TKO Area 137 Fill Bank, aircrafts and insects.
No Action and Limit Levels exceedance was recorded for operation noise monitoring in the reporting period. No action is thus required to be undertaken in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex E3.
2.3
Water Quality Monitoring
2.3.1
Surface Water Quality Monitoring
Monitoring Requirements and
Equipment
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project, impact surface water quality monitoring was carried out at the three designated surface water discharge points (i.e. DP3, DP4 and DP6) at monthly intervals during operation/ restoration phase to ensure that the SENTX will not cause adverse water quality impact. Suspension of impact surface water quality monitoring at DP3 was approved under the Baseline Monitoring Report by EPD on 24 July 2019 until the actual commencement of construction works affecting DP3 in 2022.
The parameters as listed in Table 2.22 were determined by ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. (HOKLAS Registration No. 066).
The Limit Levels of the surface water quality impact monitoring are provided in Table 2.21.
Table 2.21 Limit Levels for Surface Water Quality
|
Parameters |
Limit Level |
|
DP4 & DP6 |
|
|
Ammoniacal-nitrogen |
> 7.1 mg/L |
|
COD |
> 30 mg/L |
|
SS |
> 20 mg/L |
The locations of the monitoring stations for the Project are shown in Figure 2.1. All in situ monitoring instruments were checked, calibrated and certified by a laboratory accredited under HOKLAS or other international accreditation scheme before use, and subsequently re-calibrated at 3 monthly intervals throughout all stages of the surface water quality monitoring programme. Calibration for a DO meter was carried out before measurement according to the instruction manual of the equipment model. Details of the equipment used in the impact surface water quality monitoring works are provided in Table 2.22. Copies of the calibration certificates for the equipment are presented in Annex F1.
Table 2.22 Impact Surface Water Quality Monitoring Details
|
Monitoring Station |
Location |
Frequency |
Monitoring Dates |
Parameter |
Equipment |
|
|
DP4 |
Surface water discharge point DP4 |
Monthly |
24 Feb 2022 |
· pH · Electrical conductivity (EC) · DO · SS · COD · BOD5 · TOC · Ammoniacal–nitrogen · Nitrate-nitrogen · Nitrite–nitrogen · TKN · TN · Phosphate · Sulphate · Sulphide · Carbonate · Oil & Grease
|
· Bicarbonate · Chloride · Sodium · Potassium · Calcium · Magnesium · Nickel · Manganese · Chromium · Cadmium · Copper · Lead · Iron · Zinc · Mercury · Boron
|
YSI Professional DSS (S/N: 15H103928)
|
|
DP6 |
Surface water discharge point DP6 |
|||||
|
Notes: (a) Impact surface water quality monitoring at DP3 was suspended from the monitoring event on 25 July 2019 until the actual commencement of construction works affecting DP3 in 2022. |
||||||
Monitoring Schedule for the
Reporting Month
The schedule for surface water quality monitoring during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
Results and Observations
One monitoring event for impact surface water quality monitoring was scheduled at all designated monitoring stations during the reporting period. However, sampling could not be carried out on 24 February 2022 due to insufficient flow. Details of impact water quality monitoring event are provided in Annex F2.
No action is thus required to be undertaken in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex F3.
2.3.2
Leachate Monitoring
Monitoring Requirements and
Equipment
According to the updated EM&A Manual, continuous monitoring of leachate level and daily monitoring of effluent quality were carried out during the operation/ restoration phase.
Temperature, pH and volume of the effluent discharged from the leachate treatment plant were measured in-situ whereas the parameters as listed in Table 2.24 were determined by ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. (HOKLAS Registration No. 066).
The Limit Levels of the leachate monitoring are provided in Table 2.23.
Table 2.23 Limit Levels for Leachate Levels and Effluent Quality
|
Parameters |
Limit Level |
|
Leachate Levels |
|
|
Leachate levels above the basal liner |
1 m above the primary liner of the leachate containment system |
|
Effluent Quality |
|
|
Temperature |
> 43 °C |
|
pH Value |
6 – 10 |
|
Volume Discharged |
>1,500 m³ |
|
Suspended Solids (SS) |
> 800 mg/L |
|
Ammoniacal-nitrogen |
> 100 mg/L |
|
Nitrite-nitrogen |
> 100 mg/L |
|
Phosphate |
> 25 mg/L |
|
Sulphate |
> 900 mg/L |
|
Nitrate-nitrogen |
> 100 mg/L |
|
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) |
> 800 mg/L |
|
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) |
> 2,000 mg/L |
|
Oil & Grease |
> 20 mg/L |
|
Boron |
> 7,000 µg/L |
|
Iron |
> 7.5 mg/L |
|
Cadmium |
> 1 µg/L |
|
Chromium |
> 400 µg/L |
|
Copper |
> 1,000 µg/L |
|
Nickel |
> 800 µg/L |
|
Zinc |
> 800 µg/L |
All in situ monitoring instruments were checked, calibrated and certified by a laboratory accredited under HOKLAS or other international accreditation scheme before use, and subsequently re-calibrated at 3 monthly intervals throughout all stages of the leachate quality monitoring programme. Details of the equipment used are provided in Table 2.24. Copies of the calibration certificates for the equipment are presented in Annex F4.
Table 2.24 Leachate Levels and Effluent Quality Monitoring Details
|
Location |
Frequency |
Parameter |
Monitoring Dates |
Equipment |
|
Leachate levels above the basal liner
|
Continuous |
Leachate Levels |
1 – 28 Feb 2022 |
Pairs of pressure transducers |
|
Effluent discharged from LTP |
Daily for the first 3 months upon full operation of the LTP at wet season (Apr to Sep) and dry season (Oct to Mar), respectively and reduce to monthly thereafter subject to the monitoring results of the first 3 months for each season and agreement with the EIAO Authority, IEC and IC. (a) |
On-site Measurements: · Volume · pH · Temperature Laboratory analysis: · Suspended Solids · COD · BOD5 · TOC · Ammoniacal–nitrogen · Nitrate-nitrogen · Nitrite–nitrogen · Total Nitrogen · Sulphate · Phosphate · Oil & Grease · Alkalinity · Chloride · Calcium · Potassium · Magnesium · Iron · Zinc · Copper · Chromium · Nickel · Cadmium · Boron
|
3 – 28 Feb 2022 (b) |
Lutron WA-2017SD (S/N: T.016811)
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Note: (a) Reduction of monitoring frequency will be subject to the monitoring results to demonstrate environmentally acceptable performance. (b) Effluent monitoring was suspended on 1 and 2 February 2022 as the LTP was not in operation and no treated effluent was discharged from the on-site LTP to the foul sewer leading to Tseung Kwan O Sewage Treatment Works (TKO STW) on 1 and 2 February 2022. |
||||
Monitoring Schedule for the
Reporting Month
The schedule for leachate monitoring during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
Results and Observations
The leachate levels and effluent quality monitoring results are summarised in Table 2.25 and Table 2.26, respectively. The detailed monitoring results are provided in Annex F5 and Annex F6, respectively.
Table 2.25 Summary of Leachate Levels in the Reporting Period
|
Monitoring Location |
Average Leachate Head Levels (cm) (Range in Bracket) |
Limit Level (cm) |
|
Pump Station No. 1X (Cell 1X) |
||
|
Meter No. X-1 |
71 (53 – 97) |
> 178 |
|
Meter No. X-2 |
86 (53 – 117) |
|
|
Average |
78 (63 – 107) |
|
|
Pump Station No. 2X (Cell 2X) |
||
|
Meter No. X-1 |
85 (70 – 102) |
> 180 |
|
Meter No. X-2 |
88 (75 – 104) |
|
|
Average |
87 (73 – 103) |
|
|
Pump Station No. 3X (Cell 3X) |
||
|
Meter No. X-1 |
91 (62 – 144) |
> 175 |
|
Meter No. X-2 |
91 (62 – 144) |
|
|
Average |
91 (62 – 144) |
|
Table 2.26 Summary of Effluent Quality Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
Parameters |
Average Monitoring Results (Range in Bracket) |
Limit Level |
|
Effluent Discharged from LTP |
||
|
Temperature |
23.9°C (13.2°C – 28.6°C) |
> 43 °C |
|
pH Value |
8.5 (8.2– 8.6) |
6 – 10 |
|
Volume Discharged |
1,200m³ (385m³ - 1,496m³) |
>1,500 m³ |
|
Suspended Solids (SS) |
30.1mg/L (13.4mg/L – 52.9mg/L) |
> 800 mg/L |
|
Ammoniacal-nitrogen |
0.39mg/L (0.14mg/L – 2.73mg/L) |
> 100 mg/L |
|
Nitrite-nitrogen |
0.21mg/L (0.10mg/L – 0.67mg/L) |
> 100 mg/L |
|
Phosphate |
7.5mg/L (3.6mg/L – 9.4mg/L) |
> 25 mg/L |
|
Sulphate |
132mg/L (96mg/L – 226mg/L) |
> 900 mg/L |
|
Nitrate-nitrogen |
53.9mg/L (37.4mg/L – 72.8mg/L) |
> 100 mg/L |
|
BOD |
11mg/L (8mg/L – 22mg/L) |
> 800 mg/L |
|
COD |
913mg/L (430mg/L – 1,090mg/L) |
> 2,000 mg/L |
|
Oil & Grease |
<5mg/L (<5mg/L – 6mg/L) |
> 20 mg/L |
|
Boron |
5,137µg/L (3,210µg/L – 6,180µg/L) |
> 7,000 µg/L |
|
Iron |
1.37mg/L (0.57mg/L – 1.73mg/L) |
> 7.5 mg/L |
|
Cadmium |
<1.0µg/L (<1.0µg/L – <1.0µg/L) |
> 1 µg/L |
|
Chromium |
121µg/L (69µg/L – 142µg/L) |
> 400 µg/L |
|
Copper |
<10µg/L (<10µg/L – 68µg/L) |
> 1,000 µg/L |
|
Nickel |
111µg/L (65µg/L – 128µg/L) |
> 800 µg/L |
|
Zinc |
62µg/L (47µg/L – 92µg/L) |
> 800 µg/L |
All the leachate levels and effluent quality monitoring results were below the Limit Levels in the reporting period. No action is thus required to be undertaken in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex F3.
2.3.3
Groundwater Monitoring
Monitoring Requirements and
Equipment
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project with incorporation of the proposed updates under the Amendment Summary approved by EPD on 15 June 2020, groundwater monitoring was carried out at 14 perimeter groundwater monitoring wells (including 5 up-gradient wells and 9 down-gradient wells) (i.e. MWX-1 to MWX-14) to monitor the groundwater quality and level of the perimeter groundwater monitoring wells at monthly interval.
The Limit Levels for groundwater quality is provided in Table 2.27 below.
Table 2.27 Limit Levels for Groundwater Quality
|
Location |
Limit Levels |
|
|
Ammoniacal-nitrogen (mg L-1) |
COD (mg L-1) |
|
|
MWX-1 |
5.00 |
30 |
|
MWX-2 |
5.00 |
30 |
|
MWX-3 |
5.00 |
30 |
|
MWX-4 |
7.63 |
36 |
|
MWX-5 |
5.00 |
30 |
|
MWX-6 |
5.00 |
46 |
|
MWX-7 |
6.55 |
36 |
|
MWX-8 |
15.85 |
50 |
|
MWX-9 |
7.30 |
71 |
|
MWX-10 |
5.00 |
30 |
|
MWX-11 |
5.00 |
30 |
|
MWX-12 |
5.00 |
30 |
|
MWX-13 |
5.00 |
30 |
|
MWX-14 |
5.00 |
30 |
A bladder pump with Teflon sampling tube and adjustable discharge rates was used for purging and taking of groundwater sample from the monitoring wells. Filtered groundwater samples was collected by connecting a disposable in-line filter system to the tubing of the sampling pump, prior to storage and analysis by ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. (HOKLAS Registration No. 066).
A portable dip meter with 5mm accuracy was used for measurement of groundwater level at each well. The dip meter have an audio indicator of the water level and was checked before use.
The measurements of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were undertaken in situ. In situ monitoring instruments in compliance with the specifications listed under Section 4.3.2 of the updated EM&A Manual were used to undertake the groundwater quality monitoring for the Project.
Details of the equipment used and the monitoring locations are summarised in Table 2.28 and illustrated in Figure 2.1, respectively. Copies of the calibration certificates for the equipment are presented in Annex F7.
Table 2.28 Groundwater Monitoring Details
|
Monitoring Location |
Frequency |
Parameter |
Monitoring Dates |
Equipment |
|
|
All groundwater monitoring wells (MWX-1 to MWX-14) |
Monthly |
· Water level · pH · EC · COD · BOD5 · TOC · Ammoniacal–nitrogen · Nitrate-nitrogen · Nitrite–nitrogen · TKN · TN · Sulphate · Sulphide · Carbonate · Bicarbonate · Phosphate |
· Chloride · Sodium · Potassium · Calcium · Magnesium · Nickel · Manganese · Chromium · Cadmium · Copper · Lead · Iron · Zinc · Mercury · Boron |
15, 18 Feb 2022 |
YSI Professional DSS (S/N: 15H103928) |
Monitoring Schedule for the
Reporting Month
The schedule for surface water quality monitoring during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
Results and Observations
The groundwater quality monitoring results and detailed monitoring results are summarised in Table 2.29 and provided in Annex F8, respectively.
Table 2.29 Summary of Groundwater Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
Location |
Ammoniacal-nitrogen (mg L-1) |
COD (mg L-1) |
||
|
Monitoring Results |
Limit Levels |
Monitoring Results |
Limit Levels |
|
|
MWX-1 |
0.34 |
5.00 |
10 |
30 |
|
MWX-2 |
<0.01 |
5.00 |
4 |
30 |
|
MWX-3 |
1.25 |
5.00 |
16 |
30 |
|
MWX-4 |
7.29 |
7.63 |
43 |
36 |
|
MWX-5 |
2.39 |
5.00 |
24 |
30 |
|
MWX-6 |
3.86 |
5.00 |
50 |
46 |
|
MWX-7 |
5.70 |
6.55 |
14 |
36 |
|
MWX-8 |
14.20 |
15.85 |
45 |
50 |
|
MWX-9 |
5.14 |
7.30 |
18 |
71 |
|
MWX-10 |
0.03 |
5.00 |
10 |
30 |
|
MWX-11 |
0.12 |
5.00 |
2 |
30 |
|
MWX-12 |
<0.01 |
5.00 |
4 |
30 |
|
MWX-13 |
<0.01 |
5.00 |
5 |
30 |
|
MWX-14 |
<0.01 |
5.00 |
4 |
30 |
Limit Levels exceedances were recorded for groundwater monitoring in the reporting period and actions in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex F3 were undertaken. The groundwater quality (COD) exceedances at MWX-4 and MWX-6 on 15 February 2022 are under investigation and repeat measurement has been scheduled on 14 March 2022 to confirm findings.
The ET will keep track on the monitoring data and ensure Contractor’s compliance of the environmental requirements.
2.4
Landfill Gas Monitoring
2.4.1
Monitoring Requirements
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project, landfill gas monitoring was carried out at the perimeter of the waste boundary (monitoring wells), area between the SENTX Site boundary and the waste boundary (surface emission), occupied on-site building, service voids, utilities pit and manholes in the vicinity of the SENTX (build-up of landfill gas) during the operation/restoration phase.
The Limit Levels for landfill gas monitoring is provided in Table 2.30 below.
Table 2.30 Limit Levels for Landfill Gas Constituents
|
Parameters |
Monitoring Location |
Limit Level (% (v/v)) |
|
|
Perimeter Landfill Gas Monitoring Wells (a) |
|
||
|
Methane & Carbon Dioxide |
|
Methane |
Carbon Dioxide |
|
|
LFG1 |
1.0 |
2.2 |
|
|
LFG2 |
1.0 |
4.2 |
|
|
LFG3 |
1.0 |
6.3 |
|
|
LFG4 |
1.0 |
7.0 |
|
|
LFG5 |
1.0 |
3.4 |
|
|
LFG6 |
1.0 |
9.1 |
|
|
LFG7 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
|
|
LFG8 |
1.0 |
1.7 |
|
|
LFG9 |
2.5 |
1.7 |
|
|
LFG10 |
1.0 |
1.6 |
|
|
LFG11 |
3.0 |
2.0 |
|
|
LFG12 |
13.2 |
1.5 |
|
|
LFG13 |
22.5 |
2.7 |
|
|
LFG14 |
1.0 |
1.6 |
|
|
LFG15 |
18.2 |
2.0 |
|
|
LFG16 |
1.0 |
1.7 |
|
|
LFG17 |
10.5 |
2.1 |
|
|
LFG18 |
2.3 |
1.9 |
|
|
LFG19 |
6.3 |
3.1 |
|
|
LFG20 |
1.0 |
4.2 |
|
|
LFG21 |
1.0 |
4.3 |
|
|
LFG22 |
1.0 |
3.9 |
|
|
LFG23 |
1.0 |
10.3 |
|
|
LFG24 |
1.0 |
4.0 |
|
|
GP1 |
1.0 |
8.5 |
|
|
GP2 (shallow) |
1.0 |
11.4 |
|
|
GP2 (deep) |
1.0 |
10.4 |
|
|
GP3 (shallow) |
1.0 |
3.9 |
|
|
GP3 (deep) |
1.0 |
1.9 |
|
|
GP4 (shallow) |
1.0 |
2.3 |
|
|
GP4 (deep) |
1.0 |
5.6 |
|
|
GP5 (shallow) |
1.0 |
9.5 |
|
|
GP5 (deep) |
1.0 |
7.5 |
|
|
GP6 |
1.0 |
7.8 |
|
|
GP7 |
1.0 |
4.5 |
|
|
GP12 |
1.0 |
2.3 |
|
|
GP15 |
1.0 |
2.2 |
|
|
P7 |
1.0 |
2.5 |
|
|
P8 |
1.0 |
1.7 |
|
|
P9 |
1.0 |
2.7 |
|
Service Voids, Utilities Pits and Manholes |
|||
|
Methane (or flammable gas) |
Service voids, utilities pits and manholes |
1% by volume |
|
|
Permanent Gas Monitoring System |
|||
|
Methane (or flammable gas) |
Permanent Gas Monitoring System |
1% by volume (20% LEL) |
|
|
Area Between the SENTX Site Boundary and Waste Boundary (Surface Emission) |
|||
|
Flammable gas |
Area between SENTX site boundary and waste boundary |
30 ppm |
|
|
Notes: (a) Provisional Limit Levels established based on the pre-operation phase baseline and additional landfill gas monitoring results in the Pre-operation Baseline Monitoring Report. |
|||
Gas analysers in compliance with the specifications listed under Section 5.4.1 of the updated EM&A Manual were used to monitor the gas parameters at the landfill gas monitoring wells, service voids, utilities pits and manholes. The gas analyser was calibrated by a laboratory accredited under HOKLAS at yearly intervals and checked before use to ensure the validity and accuracy of the results. A portable dip meter was used to monitor the water level in the monitoring wells.
Permanent gas monitoring systems with pre-set alarm levels for methane at 20% lower explosive limit (LEL, equivalent to 1% methane gas (v/v)) were installed and operated in all occupied on-site buildings at SENTX. A central control panel is equipped to alert site personnel when the gas concentration at any detector reaches the alarm level.
Flammable gas detector in compliance with the specifications listed under Section 5.4.1 of the updated EM&A Manual was used to measure flammable gas concentration. Flammable gas surface emission survey was conducted at a slow pace with the inlet tube of the meter probe a few centimeters above ground surface to detect flammable gas emitted from the ground surface.
Bulk gas samples were collected into inert sample containers (i.e. Tedlar Bag) and transferred to ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd. (HOKLAS Registration No. 066) laboratory within 24 hours of collection for direct analysis on a gas chromatography within 48 hours after collection.
The equipment used in the landfill gas monitoring programme is summarised in Table 2.31. The landfill gas monitoring locations for perimeter landfill gas monitoring wells, area between SENTX site boundary and waste boundary (surface emission) and service voids, utilities and manholes along the Site boundary and within the SENTX site are illustrated in Figure 2.3 – 2.4, Annex G1, respectively. Copies of the calibration certificates for the equipment are presented in Annex G2.
Table 2.31 Landfill Gas Monitoring Details
|
Monitoring Location |
Frequency |
Parameter |
Monitoring Dates |
Equipment |
|
Perimeter landfill gas monitoring wells (LFG1 to LFG24, P7 to P9, GP1 to GP7, GP12 and GP15)
|
Monthly |
Ÿ Methane Ÿ Carbon dioxide Ÿ Oxygen Ÿ Atmospheric pressure |
9 Feb 2022 |
GA5000 (S/N: G507306) |
|
Service voids, utilities and manholes along the Site boundary and within the SENTX Site (UU1 to UU28) |
Monthly |
Ÿ Methane Ÿ Carbon dioxide Ÿ Oxygen |
11 Feb 2022 |
GA5000 (S/N: G507306) |
|
Permanent gas monitoring system in all occupied on-site buildings |
Continuous |
Ÿ Methane (or flammable gas) by permanent gas monitoring system |
1 – 28 Feb 2022 |
Permanent gas monitoring system |
|
Areas between the SENTX Site boundary and the waste boundary and location of vegetation stress |
Quarterly |
Ÿ Flammable gas emitted from the ground surface |
15 Feb 2022 |
GMI Leak Surveyor (S/N: 554846) |
|
Bulk gas sampling at least 2 of the perimeters LFG monitoring wells |
Quarterly |
Ÿ Methane Ÿ Carbon dioxide Ÿ Oxygen Ÿ Nitrogen Ÿ Carbon monoxide Ÿ Other flammable gas |
16 Feb 2022 |
Gas sampling pump and Tedlar bags |
Monitoring Schedule for the
Reporting Month
The schedule for landfill gas monitoring during the reporting period is provided in Annex C.
Results and Observations
The landfill gas monitoring results are summarised and provided in Tables 2.32 - 2.35 and Annex G3, respectively.
Table 2.32 Summary of Landfill Gas Monitoring Results at Perimeter LFG Monitoring Wells in the Reporting Period
|
Location |
Methane (% (v/v)) |
Carbon Dioxide (% (v/v)) |
||
|
Monitoring Results |
Limit Levels (a) |
Monitoring Results |
Limit Levels (a) |
|
|
LFG1 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
2.2 |
|
LFG2 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
4.2 |
|
LFG3 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.9 |
6.3 |
|
LFG4 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
7.0 |
|
LFG5 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.3 |
3.4 |
|
LFG6 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
9.1 |
|
LFG7 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
1.5 |
|
LFG8 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
1.7 |
|
LFG9 |
0.0 |
2.5 |
0.1 |
1.7 |
|
LFG10 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
1.6 |
|
LFG11 |
0.0 |
3.0 |
0.2 |
2.0 |
|
LFG12 |
0.0 |
13.2 |
0.1 |
1.5 |
|
LFG13 |
6.2 |
22.5 |
0.9 |
2.7 |
|
LFG14 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
1.6 |
|
LFG15 |
0.0 |
18.2 |
0.3 |
2.0 |
|
LFG16 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
1.7 |
|
LFG17 |
0.0 |
10.5 |
0.1 |
2.1 |
|
LFG18 |
0.0 |
2.3 |
0.1 |
1.9 |
|
LFG19 |
0.0 |
6.3 |
0.1 |
3.1 |
|
LFG20 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.7 |
4.2 |
|
LFG21 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
2.1 |
4.3 |
|
LFG22 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
1.8 |
3.9 |
|
LFG23 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.9 |
10.3 |
|
LFG24 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.8 |
4.0 |
|
GP1 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
8.5 |
|
GP2 (shallow) |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
11.4 |
|
GP2 (deep) |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
10.4 |
|
GP3 (shallow) |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
3.9 |
|
GP3 (deep) |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.7 |
1.9 |
|
GP4 (shallow) |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.2 |
2.3 |
|
GP4 (deep) |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
5.6 |
|
GP5 (shallow) |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
9.5 |
|
GP5 (deep) |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
7.5 |
|
GP6 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
6.7 |
7.8 |
|
GP7 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.2 |
4.5 |
|
GP12 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.2 |
2.3 |
|
GP15 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
2.2 |
|
P7 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
2.5 |
|
P8 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
1.7 |
|
P9 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
2.7 |
|
Notes: (a) Provisional Limit Levels established based on the pre-operation phase baseline and additional landfill gas monitoring results in the Pre-operation Baseline Monitoring Report. |
||||
Table 2.33 Summary of Landfill Gas Monitoring Results at Service Voids, Utilities Pits and Manholes in the Reporting Period
|
Location |
Methane (% (v/v)) |
|
|
Monitoring Results |
Limit Levels |
|
|
UU01 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU02 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU03 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU04 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU05 |
0.1 |
1.0 |
|
UU06 |
0.1 |
1.0 |
|
UU07 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU08 |
0.1 |
1.0 |
|
UU09 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU10 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU11 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU12 |
Voided due to latest site programme and on-going operation work |
1.0 |
|
UU13 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU14 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU15 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU16 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU17 |
Voided due to latest site programme and on-going operation work |
1.0 |
|
UU18 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU19 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU20 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU21 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU22 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU23 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU24 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU25 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU26 |
0.2 |
1.0 |
|
UU27 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
|
UU28 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
Table 2.34 Summary of Landfill Gas Bulk Gas Sampling Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
Parameters |
Limit Level (LFG14) (a) |
LFG14 |
Limit Level (LFG15) (a) |
LFG15 |
|
Methane (% (v/v)) |
1.0 |
0.0 |
18.2 |
0.0 |
|
Carbon Dioxide (% (v/v)) |
1.6 |
0.119 |
2.0 |
0.110 |
|
Oxygen (% (v/v)) |
- |
10.2 |
- |
20.1 |
|
Nitrogen (% (v/v)) |
- |
90.5 |
- |
80.3 |
|
Carbon Monoxide (% (v/v)) |
- |
<0.020 |
- |
<0.020 |
|
Hydrogen (% (v/v)) |
- |
<0.020 |
- |
<0.020 |
|
Ethane (ppmv) |
- |
<1.0 |
- |
<1.0 |
|
Propane (ppmv) |
- |
<1.0 |
- |
<1.0 |
|
Butane (ppmv) |
- |
<1.0 |
- |
<1.0 |
|
Notes: (a) Provisional Limit Levels established based on the pre-operation phase baseline and additional landfill gas monitoring results in the Pre-operation Baseline Monitoring Report. |
||||
Table 2.35 Summary of Flammable Gas Surface Emission Monitoring Results in the Reporting Period
|
GPS Coordinates Latitude (N) |
Longitude (E) |
Monitoring Results (ppm) |
Limit Level (ppm) |
|
22o16’36” |
114o16’36” |
3 |
30 |
|
22o16’24” |
114o16’36” |
6 |
|
The alarm of the permanent gas monitoring systems with pre-set levels for methane at 20% lower explosive limit (LEL, equivalent to 1% methane gas (v/v)) was not triggered at all occupied on-site buildings at SENTX in February 2022.
All the landfill gas monitoring results were below the Limit Levels in the reporting period. No action is thus required to be undertaken in accordance with the Event and Action Plan presented in Annex G4.
2.5
Landscape and Visual Monitoring
2.5.1
Monitoring Requirements
According to the updated EM&A Manual of the Project, the monthly landscape and visual audit was conducted on 24 February 2022 to monitor the implementation of the landscape and visual mitigation measures during operation/ restoration phase.
All relevant environmental mitigation measures listed in the approved EIA Report and the updated EM&A Manual and their implementation status are summarised in Annex B.
2.5.2
Results and Observations
The Contractor has implemented environmental mitigation measures as stated in the approved EIA Report and the EM&A Manual.
Regarding the landscape and visual audit, the Contractor was reminded to maintain the advance screen planting works regularly to ensure effective screening of views of project works from the High Junk Peak Trail.
2.6
EM&A Site Inspection
Site inspections were carried out on a weekly basis with the Contractor, IEC and ER to monitor the implementation of proper environmental pollution control and mitigation measures under the Project. In the reporting period, 3 site inspections were carried out on 10, 17 and 24 February 2022.
Key observations during the site inspections are summarised in Table 2.36.
Table 2.36 Key Observations Identified during the Site Inspection in this Reporting Month
|
Inspection Date |
Environmental Observations and Recommendations |
|
10 February 2022 |
· The Contractor shall provide a NRMM label on the crane near sump house 4. · The Contractor shall remove the general refuse accumulated at the channel near sump house 3 and dispose of the waste regularly to minimise odour and pest issues. |
|
17 February 2022 |
· The Contractor shall provide drip tray for the chemical stored near X10a. · The Contractor shall remove the general refuse accumulated near X10a, Cell 3X perimeter bund and at the channel near sump house 3 and VWF, and dispose of the waste regularly. |
|
24 February 2022 |
· The Contractor shall cover the water tank near sediment trap with lid to minimise pest issues. · The Contractor shall remove the stagnant water accumulated at the channel near sump house 3 and at Cell 4X regularly and spray larvicides for mosquito control, if necessary. · The Contractor shall remove the stagnant water accumulated in the drip trays at Wetsep near sediment trap. |
The Contractor has rectified most of the observations identified during environmental site inspections in the reporting period. Key environmental deficiencies identified and the corresponding rectification actions are presented in Table 2.37.
Table 2.37 Summary of Environmental Deficiencies Identified and Corresponding Rectification Actions
|
Deficiencies |
Rectifications Implemented |
Proposed Additional Control Measures |
|
Surface Water |
||
|
Intercepting channels & drainage system |
Ÿ Reviewed drainage plan. |
Ÿ Addition of channels. Ÿ Expedite the construction of permanent sediment trap and discharge culverts.
|
|
DP channels (design & regular silt removal) |
Ÿ Carried out regular maintenance and cleaning of channels. Ÿ DP4 channel: Area near the channel was paved with concrete and a bund was built. Ÿ DP6 channel: Gravel piles on the channel were covered with concrete which serve as blocks for running water and to divide the channel into several sections. A pump was placed in the water zone in the upstream section to pump water to the Wetsep for treatment prior to the discharge to the last section before the weir plate. Ÿ DP6: Pipes through the gravel piles between different channel sections were covered with geotextiles to block debris and silt.
|
N.A. |
|
Stockpiles & exposed soil |
Ÿ Installed silt fencing near surface water channel along DP6 channel. |
Ÿ Improve soil covering. Ÿ Compaction and cover for stockpiles and soil slopes.
|
|
Wetsep (treatment capacity & number) |
Ÿ Reviewed Wetsep capacity. Ÿ Chemicals dosage of the Wetsep was increased to enhance the efficiency. |
Ÿ Install additional Wetsep. |
|
Backflow / ponding during heavy rainfall |
Ÿ Raised with EPD (LDG) and CEDD. |
N.A. |
2.7
Waste Management Status
The Contractor has registered as chemical waste producer under the Contract. Sufficient numbers of receptacles were available for general refuse collection and sorting.
As informed by the Contractor, waste generated during this reporting period include mainly inert C&D materials. Reference has been made to the waste flow table prepared by the Contractor. The quantities of different types of wastes and imported fill materials are summarised in Table 2.38.
Table 2.38 Quantities of Different Waste Generated and Imported Fill Materials
|
Month/ Year |
Inert C&D Materials (a) (in ‘000m3) |
Imported
Fill |
Inert
Construction Waste Re-used |
Non-inert
Construction Waste (c) |
Recyclable Materials (d) (in ‘000kg) |
Chemical
Wastes |
|
|
Rock |
Soil |
||||||
|
1 – 28 Feb 2022 |
1.284 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.016 |
0 |
0.460 |
|
Notes: (a) Inert construction wastes include hard rock and large broken concrete, and materials disposed as public fill. Density assumption: 1.6 (kg/L) for public fill. (b) Imported fill refers to materials generated from other project for on-site reuse. (c) Non-inert construction wastes include general refuse disposed at landfill. Density assumption: 0.9 (kg/L) for general refuse. (d) Recyclable materials include metals, paper, cardboard, plastics and others. |
|||||||
2.8
Implementation Status of
Environmental Mitigation Measures
A summary of the Environmental Mitigation Implementation Schedule is presented in Annex B. The necessary mitigation measures were implemented properly for the Project.
2.9
Summary of Exceedances of the Environmental Quality
Performance Limit
The operation/ restoration phase air quality, noise and landfill gas monitoring results complied with the Action and Limit Levels in the reporting period. Two exceedances of the Limit Level for groundwater (COD) were recorded for water quality impact monitoring in the reporting period. The groundwater (COD) exceedances at MWX-4 and MWX-6 on 15 February 2022 are under investigation.
Cumulative statistics on exceedances is provided in Annex H.
2.10
Summary of Complaints, Notification of Summons and
Successful Prosecutions
There were no complaints, notification of summons or prosecution recorded in the reporting period.
Statistics on complaints, notifications of summons, successful prosecutions are summarised in Annex H.
3
Future Key Issues
3.1
Construction Programme for the Coming Month
As informed by the Contractor, the major works for the Project in March 2022 will be:
Ÿ Excavation and removal of unsuitable fill materials;
Ÿ Import materials for Cell 4X;
Ÿ Construction of Cell 4X formation;
Ÿ Liner works at Cell 4X;
Ÿ Construction of perimeter bund along the West side of Cell 4X;
Ÿ Equipment installation at pump house 4;
Ÿ Utilities installation along the perimeter channel at Western bund of Cell 4X;
Ÿ Defects rectification for waste reception area, including weighbridge, vehicle washing facilities, wheel wash bay and guard house;
Ÿ Defects rectification for infrastructure buildings;
Ÿ Defects rectification for pavement works at Part X1 area;
Ÿ Defects rectification for surface water channels along the road pavement;
Ÿ Installation of the remaining LFG and leachate HDPE pipes at Cell 4X;
Ÿ Construction of MSE wall; and
Ÿ Landscape work.
3.2
Key Issues for the Coming Month
Potential environmental impacts arising from the above upcoming construction activities in the next reporting period of March 2022 are mainly associated with dust emission from the exposed area and loading and unloading operation of dusty materials. The ET will keep track on the construction and operation works to confirm compliance of environmental requirements and the proper implementation of all necessary mitigation measures.
3.3
Monitoring Schedule for the Coming Month
The tentative schedule for environmental monitoring in March 2022 are provided in Annex I.
4
Conclusion and Recommendation
This EM&A Report presents the findings of the EM&A activities undertaken during the period from 1 to 28 February 2022 in accordance with the updated EM&A Manual and the requirements of the Environmental Permit (EP-308/2008/B).
Air quality (24-hour TSP, odour, thermal oxidiser, landfill gas flare and landfill gas generator stack emission, ambient VOCs , ammonia and H2S), noise, water quality (surface water, leachate and groundwater) and landfill gas monitoring were carried out in the reporting period. Results for air quality, noise and landfill gas monitoring complied with the Action and Limit Levels in the reporting period. Two exceedances of the Limit Level for groundwater (COD) were recorded in the reporting period.
Environmental site inspections were carried out during the reporting period. Recommendations on remedial actions were given to the Contractor for the deficiencies identified during the site inspections.
There were no complaints, notification of summons or prosecution recorded in the reporting period.
The ET will keep track on the construction and operation/restoration works to confirm compliance of environmental requirements and the proper implementation of all necessary mitigation measures.